Perch is a popular fish for many, not just to fish but also to eat, there are types of perch found in North American Waters. They can be found in salt and fresh water. Some species reside in both. This article will discuss the four major species, including information about where they are located their taste, and much more. Here are different types of perch found in North American Waters.

Types of Perch
4 Types of Perch to catch
YELLOW PERCH
Yellow perch (Perca flavescens) is commonly referred to by the names perch, stripe, or perch largemouth bassor mantis is a perciform fish native to a large portion of North America. It was first described in 1814 in the work of Samuel Latham Mitchill of New York.
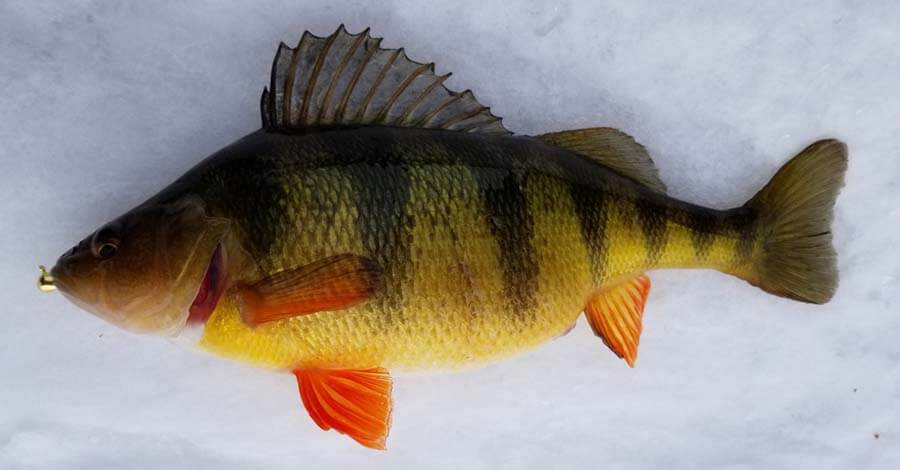

YELLOW PERCH
The species is similar and morphologically akin to the European perch (Perca fluviatilis) and is often considered a different species from its European counterpart. Other names commonly associated with yellow perch are coontail, largemouth bass lake perch, and raccoon perch.
Appearance
The yellow perch is an elongated oval body with a large but blunt snout that does not extend past the upper jaw. Similar to most perches, it is equipped with two distinct dorsal fins. The anterior or the first dorsal fin comprises 12-14 spines.
The second fin has 2-3 spines on the front, followed by 12-13 soft rayons. The anal fin contains two spines and 7 soft Rays. The upper portion of the body and head can vary in hues, ranging from bright to golden green or olive. They are usually golden yellow.
Color
The color of the upper part of the body extends to the flanks, where it creates the appearance of six to eight vertical bars set against a background of yellowish-green or yellowish. They typically have a blackish spot on the surface of the initial dorsal fin between the 4 or 3 posterior spines.
The color of caudal and dorsal fins ranges between green and yellow, and the pelvic and anal fins may range from white or silvery yellow. The pectoral fins are translucent and amber-colored. The ventral portion of the human body is white. Younger fish are more pale and can have an almost translucent background color.
Size
The longest length recorded was fifty centimeters (20 in); however, more often, it’s around 19.1 centimeters (7.5 in), and the highest reported weight can be 1.9 kilograms (4.2 pounds). ).
Origin appeared
Yellow perch is one of only four perch types found in North America. They are native to the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, Great Lakes basins, St. Lawrence, and Mississippi rivers. In Canada, the range of its native habitat covers Nova Scotia and Quebec north towards the Mackenzie River.
It is also common as far north in Great Slave Lake and as much to the west as Alberta. It isn’t native to other regions of Canada. Within the United States, the native range extends southwards towards Ohio and Illinois and across most of the northeastern United States.
It is also thought to be native to the part of the Atlantic Slope watershed, which extends southward to and includes the Savannah River. Also, there is a smaller native population in The Dead Lakes region of Florida’s Apalachicola River system.
Yellow perch are also extensively introduced to commercial and sport fishing goals; the types have also been introduced as a food basis for bigmouth bass and walleye. The introductions were primarily via the US Fish Commission in the early and late 19th century.
However, illegal introductions could result from dispersal across connected waterways or live baiting. There are isolated populations in the southwestern and northwestern parts of the United States. Yellow perch hasn’t yet had a chance to be introduced in North America. Introductions to Canada have been more limited than those in the United States. It is now extinct in Arkansas.
WHITE PERCH
The white perch (Morone americana) is not a types of perch but rather a member of the family of bass that is temperate, Moronidae, notable as game fish and food fish in the eastern part of North America. Some places are incorrectly identified as “Silver bass.” It is usually silvery-white in appearance, so it’s called that, according to the environment and size.
However, specimens are beginning to show dark hues near the dorsal fin and around the sides part of the animal. They are sometimes given the name “blackbacks.” White perch measure as large as 49.5 centimeters (19.5 in) in length and weigh 2.2 kg (4.9 lbs).

WHITE PERCH
Habitat
While it is a fan of salty water, it can also be located in coastal and freshwater areas extending from up to the St. Lawrence River and Lake Ontario south to the Pee Dee River in South Carolina and Nova Scotia.
They can also be located within the Lower Great Lakes, Finger Lakes, Long Island Sound, and adjacent coastal areas, including the Hudson and Mohawk rivers, Delaware Bay, and Chesapeake Bay.
They are also found in small lakes and ponds. Raw meat can appear pink but transparent and clear when cooked. Sometimes, a parasite named Lironeca ovalis is found within the gills. They only limit the rate of growth for white perch.
White perch feed on eggs of many species that are native to the Great Lakes, such as walleye and other types of perch are real. Fish eggs can comprise the sole source of food for them. They are fans of tiny minnows, such as fathead and mud minnows.
Their food
White perch typically feeds on shrimp, razor clams, razors, and bloodworms. They are all native to this region. White perch can be a thriving type. Females can lay over 150,000 eggs in a single period of spawning that lasts less than a week.
Some males can help the spawning female and may each fertilize a small portion of the eggs. The eggs hatch within a period of one to seven days post-fertilization. They are recovering from a population loss within the Hudson River.
White perch are considered a nuisance species in certain states because of their capacity to degrade fishing habitats. They are associated with the decline of white bass and walleye populations due to their heavy consumption of baitfish used by these species and can compete for space and food.
Numerous states have passed laws that prohibit keeping live perch. In addition, these states have recommended that the caught white perch be released back into the waters to stop spreading.
SILVER PERCH
The SILVER PERCH (Bairdiella Chrysoura) is an American fish type that originated in the US. The species is abundant along the east coast, and in the Gulf of Mexico, silver perch are usually caught by inshore fishermen searching for larger species.

SILVER PERCH
Size
It is rare for this fish to reach 9 inches (230 millimeters). Yellowtail is a scarce food source as it is great table food and part of any southern fall fry. Also known as largemouth bass
Appearance
A wide terminal mouth characterizes the largemouth bass raised slightly obliquely. The lower jaw is larger than the jaw on top. The barbel doesn’t bear an actual bar. Still, it does possess 3 pairs of brain pores (the arrangement of the pores of the barbels and beneath-barbel allows for a way of distinguishing between various families of Sciaenidae).
The preoperculum, the bony plate located just before the operculum, contains some spines set at an angle. The dorsal part of the fin has 10 to 11 spines and nineteen to 23 soft Rays. The anal fin comprises two spines, one of which is sharper and greater than two-thirds of in length as long as the soft ray that first and up to ten soft rays.
The fish has a two-chambered swim bladder attached via an inner ear. It can hear well, comparable to the goldfish (Carassius auratus), and is renowned for hearing. Its color is generally silvery, greenish, or blueish on the dorsal face and yellowish or silvery underneath. The fins appear yellowish or grayish.
Habitat
Silver perch are indigenous to that region of the United States East Coast. The range of the silver perch is extensive, from New York to Florida, the Gulf of Mexico, and Mexico. They can be found near the shoreline in seagrass beds, rivers, tidal streams, and mudflats.
Spawning is common in the shallow, saline areas of coastal bays and areas; it is most active from May to September. Silver perch matures during the third or second season (by about 6 inches). Adults consume crustaceans and smaller fish. They can live for up to six years. This species is not eligible for inclusion in a state-wide registry.
WALLEYE
Walleye (Sander vitreus synonym Stizostedion vitreum). Also known as yellow pike or yellow pike, it is a perciform freshwater fish native to the majority parts of Canada as well as the Northern United States.
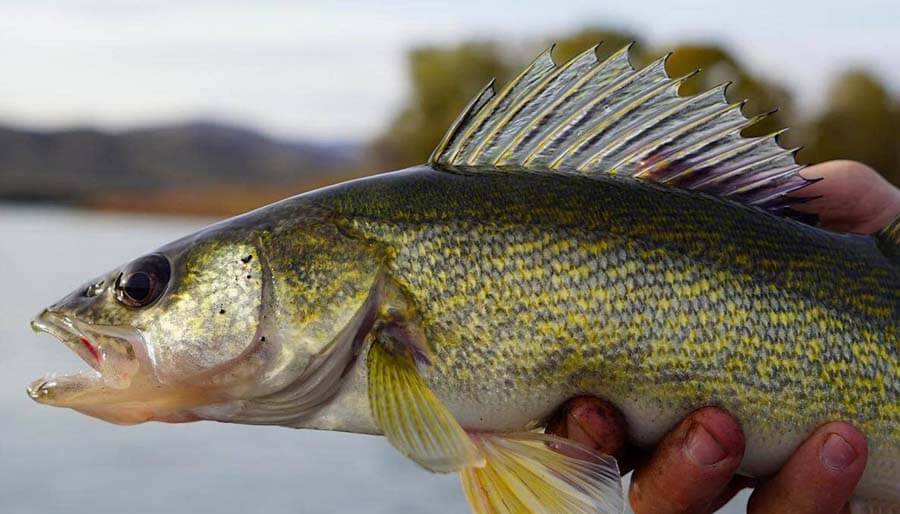

Walleyes in Rivers
It is a North American close relative of the European walleye, which is also known by the name of walleye. The walleye is often called yellow walleye to differentiate them from the blue one. Which was once a subspecies located throughout Southern Ontario in the southern Ontario and Quebec regions. However, it is now believed to be extinct.
However, the recent genetic analysis of the preserved (frozen) portion of the blue walleye’ has revealed that the blue and yellow walleye. Are different phenotypes of the same species and don’t require a distinct taxonomic classification?
Habitat
The Walleyes display a variety across watersheds. The fish in a watershed have much in common and are genetically different from those in nearby watersheds. It has been propagated artificially for over 100 years and is placed on top of the existing population or introduced to waterways naturally empty of the species. Often, this reduces the genetic makeup of the population.
The term “zander” originates from the pearly eyes due to the reflective tapetum lucidum that can also allow it to view clearly in dim light. They also give the eyes an edgy and somber appearance. Your vision affects your behavior.
Avoid bright lights and feed on fish that do not perceive as clearly as they should. Many anglers search for walleyes in the evening since this is when the most food production happens. The fish’s eyes enable them to see easily in murky waters (stained or rough breaking water), giving them an advantage over their predators.
Thus, anglers who fish for walleyes typically search for areas where a nice “walleye chop” (i.e., rough water) can be observed. Their eyes also allow fish to inhabit the deeper parts of a lake. It is often seen in deeper waters, particularly during the summer and night.
Color
Walleyes are predominantly olive-colored and gold-colored (hence their French common name: dore, gold). The dorsal aspect of the walleye is olive in hue, but it changes to gold along the flanks. The pattern of gold and olive is separated by five frames darker than the rest, which extend to the higher sides.
The color changes to white on the belly. In the mouth, a walleye can be big and armed with many sharp teeth. The first dorsal, as well as anal fins, are spiny like the operculum. Walleyes can be distinct from their close relatives, the Saucer, due to the white coloration on the lower portion of their caudal fin, which is not present within the Saucer.
Additionally, the dorsal and the caudal fins in the saucers are adorned with distinct black dots, which are not visible or obscure on the walleye’s fins.
Size
Walleyes can grow up to 80 centimeters (31 inches) in length and weigh around 9 kg (20 pounds). The largest size recorded of the fish was 107 centimeters (42 inches) in length and 13 kilograms (29 pounds) in weight.
The amount of fish caught depends on the location within their range. The populations in the south are typically expanding faster and becoming larger. Females generally grow bigger than males. Walleyes can live for a long time.
The maximum age recorded is 29 years old. Only a few walleyes live longer than six or five years in heavily over-exploited populations. Within North America, where they are extremely sought-after. The size they average when caught is on an average of 30 to 50 centimeters (12 to 20 inches), considerably less than their maximum size.
FAQs about Perch
What’s the taste of perch?
The perch’s meat is skinny, but it is also steady. It is cooked in batter or grilled or baked. It is mild in flavor and delicious with various toppings and rich sauces.
What is the food perch eat?
Like other fish species, young specimens eat plankton. Adult fish consume a broad assortment of food items, from surface insects and other invertebrates to smaller fish. Large perch are primarily carnivores.
What type of fish is perch?
Perch is a white-colored fish with extremely low fat content. It contains less than 2 grams of fat for 100 grams. It is recommended for those suffering from weight gain problems, which require adherence to an eat-low-caloric diet if gentle methods are used to prepare it.
Where are perch fish raised?
They are freshwater and aquaculture-raised species of fish that originate from faraway countries. The panga is reared within the Mekong River (Vietnam), and the perch is found on the shores of Lake Victoria in Africa.
Maybe you like:
- 15 Types of Flatfish to Catch in the Ocean: Complete Guide
- 12 Types of Snapper to Catch In Florida: The Quick Guide
- The 23 Types of Trout Species
- Can Dogs Eat Trout? Is it safe to eat?