There are some myths and legends surrounding the Biggest Sharks in the World. In reality, you don’t have to be a shark expert to tell you what some of the largest sharks are. This article will give you an insight into what you need to know about these majestic creatures. Then, you can start a conversation about these fascinating creatures! Listed below are some of the largest sharks on the planet.
Biggest Sharks In The World! Top 10 Rankings
The Bigeye Thresher Shark is 15.1 feet long. The Bluntnose Sixgill Shark is 15.8 feet long. The Great Hammerhead is 20 feet long. The Pacific Sleeper Shark is 23 feet long. The Great White Shark is almost forty feet long. Finally, the Whale Shark measures 41 feet long. You can see how impressive these creatures can be. Once you get to know them, you’ll be fascinated by their size.
What Is The Biggest Sharks Ever Known In The World?
According to new research, megalodons may have been the largest sharks ever known to man in this world, but this isn’t true. Megalodons, which lived approximately 15 to 3.6 million years ago, were large enough to weigh 50 tons. Female Megalodons were larger than males, between 44 and 56 feet long. Estimates of Megalodon’s length come from correlations between tooth size and shark body length.
Megalodon’s diet consisted of fish, including tuna. Megalodon required around 2,500 pounds of food a day. Its jaws were so large they could swallow two adults side-by-side. Megalodon had over a foot-long tooth, making it a formidable predator. But, despite its gigantic size, it had trouble surviving in the colder waters of the world.
What Are The Smallest Sharks Ever Known In The World?
Although it’s impossible to find a definitive answer to the question “What is the smallest shark ever known?” it’s possible to come close. The dwarf lantern shark is a species of shark with only one confirmed specimen worldwide. At approximately sixteen to seventeen centimeters (6.3-6.8 inches), it’s a relatively small, ovoviviparous shark. The species feeds primarily on crustaceans and reaches sexual maturity between 7.5 and nine inches long. It lives in deep water and is largely protected from commercial fisheries, but the research needs to be done more thoroughly to determine how common it is.
Megalodon had a huge jaw. Its jaw would have measured 2.7 by 3.4 meters, with two hundred and sixty-six teeth. Scientists estimate the bite force of the megalodon to be between eighty-five and eighty-two Newtons. The megalodon’s jaw could reach this size, so it likely ate large fish, dolphins, and whales. The megalodon’s jaw was so big that it ate many other animals, including whales.
The Top 10 Biggest Sharks In The World
This article will give you a brief description of the top ten biggest sharks in the world. Below are the names and sizes of the biggest sharks known to man. This list includes the Great White shark, the most terrifying of all sharks. This mackerel shark belongs to the species known as the great white, and its preferred prey is herring and sardines. Unlike other great white sharks, it has no real ocean predators and a range of more than a thousand meters.
Whale Shark Rhincodon Typus 55.7 Feet / 17 M
The whale shark is one of the largest fish species in the world today. Its average length is about 55.7 feet / 17 meters, and its maximum recorded weight is around 47,000 pounds. The whale shark is a filter feeder found in the open ocean.

It is the largest extant species in its family and is the largest non-mammal vertebrate in the animal kingdom. The whale shark is the only extant member of the family Rhincodontidae and belongs to the subclass Elasmobranchii. This fish belongs to the same family as the Pacific sleeper and Greenland sharks.
The mouth of the whale shark contains over three hundred rows of tiny teeth and twenty filter pads. The mouth of the whale shark is located on the front of the head, not on the underside.
It measures approximately 1.55 meters across. Its head is broad and flat and features two tiny eyes on the front corners. Its five pairs of dorsal fins are at the body’s back. The whale shark has a semi-lunate tail with a prominent checkerboard pattern.
Basking Shark Cetorhinus Maximus 49.8 Feet
The Basking Shark is a slow-moving fish species from the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. This species is most often found near the ocean surface and can grow to over 40 feet in length and weigh over five tons.

Basking Shark Cetorhinus Maximus
Its substantial body and massive gill rakers help it filter food, and it can cover over 9,000 km in a single year. The Basking Shark is considered one of the world’s largest fish, second only to the whale shark.
The Basking Shark’s size is not the only fascinating aspect of its existence. They migrate across the entire ocean basins in search of plankton sources. This is one of the reasons their populations increase in the summer in both hemispheres. However, their mating habits remain unknown.
For now, this species is best known for its ability to reproduce. Unlike other sharks, basking sharks reproduce via asexual methods. They give birth to one or two live pups, each two to four years. Their lifespan is estimated to be between 50 years. Basking sharks are considered social animals and live in schools. They also tend to live in communities that are divided by sex.
Megamouth Shark Megachasma Pelagios 25 Feet
The Megamouth Shark is a brown shark with a whitish underbelly. Despite its name, this species is not commonly seen near the surface. Because of this, it is often overlooked and stays out of sight.
Known to inhabit oceans in temperate regions, megamouths are commonly seen off the coasts of Australia, Africa, the Philippines, and Mexico. They feed on krill, jellyfish, and copepods. While they can grow to be 18 feet long and weigh more than two thousand pounds, the Megamouth is considered a gentle species.

Megamouth Shark Megachasma Pelagios
This slender megamouth shark has 50 rows of teeth in its upper and lower jaws. Its glowing mouth draws in small sea life, which swims into its mouth without realizing it is there. The Megamouth Shark belongs to the Megachasmidae family and the Chondrichthyes class. Its size is an indication of its importance in the ocean.
Tiger Shark Galeocerdo Cuvier 24 Feet
The tiger shark, scientifically known as Galeocerdo Cuvier, is a large predatory fish that lives in the waters off Hawaii and the Hawaiian Islands. Its size is estimated to be about 24.6 feet long. They are classified as near threatened by the World Conservation Union, though they do not face an immediate threat of extinction.

Tiger Shark Galeocerdo Cuvier
The scientific name of the tiger shark is Galeocerdo cuvier, derived from the Greek words galeus and cerdo. Its name is given to it because it is known to be a voracious predator.
It is known to grow to over five meters and is often found around the islands of central Pacific waters. Its stripes, which fade in and out over time, are one of the tiger shark’s most distinctive characteristics.
Greenland Shark Somniosus Microcephalus 24 Feet
The Greenland shark is a species of fish. Its lifespan varies between 335 and 392 years, with an estimated doubling time of 14 years. Its primary uses are for fisheries in Greenland, Iceland, and Norway. They are also caught for their meat, liver oil, and hide. While shark flesh is highly toxic to humans, it can be treated. The resulting dish is known as Hakarl.

Greenland Shark Somniosus Microcephalus
The scientific name of the Greenland shark is Somniosus microcephalus, derived from the Latin word “somnia.” The New Latin term “microcephalus” means “tiny head.” The species is the largest, growing up to 24 feet long. It is larger than its male counterpart. Female Greenland sharks are pregnant for up to eight years before giving birth.
Great White Shark Carcharodon Carcharias 20 Feets
The Great White Shark (Carcharodon carcharias) is one of the most recognizable shark species. This species originated in the Late Miocene and lived for over 30 years.
The Great White Shark can grow up to 6.5 meters in length. This predator eats eggs produced in the uterus and swallows the teeth shed in the womb during development. Litters of one or more pups are produced yearly, with each litter comprising two to ten pups.

Great White Shark Carcharodon Carcharias
The Great White Shark is widely distributed in both tropical and cold-temperate waters. Known to visit tropical islands and swim below the surface, it can be found all over the world. It is also found in the Caribbean, the Pacific Ocean, and the Mediterranean Sea.
It is the largest shark in its class and can be found in any ocean, but it is more common in cooler regions of the world. This shark is often seen near Florida, Newfoundland, and the Aleutian Islands’ shores.
Great Hammerhead Shark Sphyrna Mokarran 20 Feets
The great hammerhead shark is a large, charismatic predator that can grow up to 20 feet long and six meters (ten meters). They are commonly encountered in deep and coastal waters and migrate widely to feed.
The predator uses highly evolved head weapons to pin down its prey and consume stingrays. Its natural habitat ranges from North America’s warm coastal waters to the Pacific Ocean’s warm tropical waters.
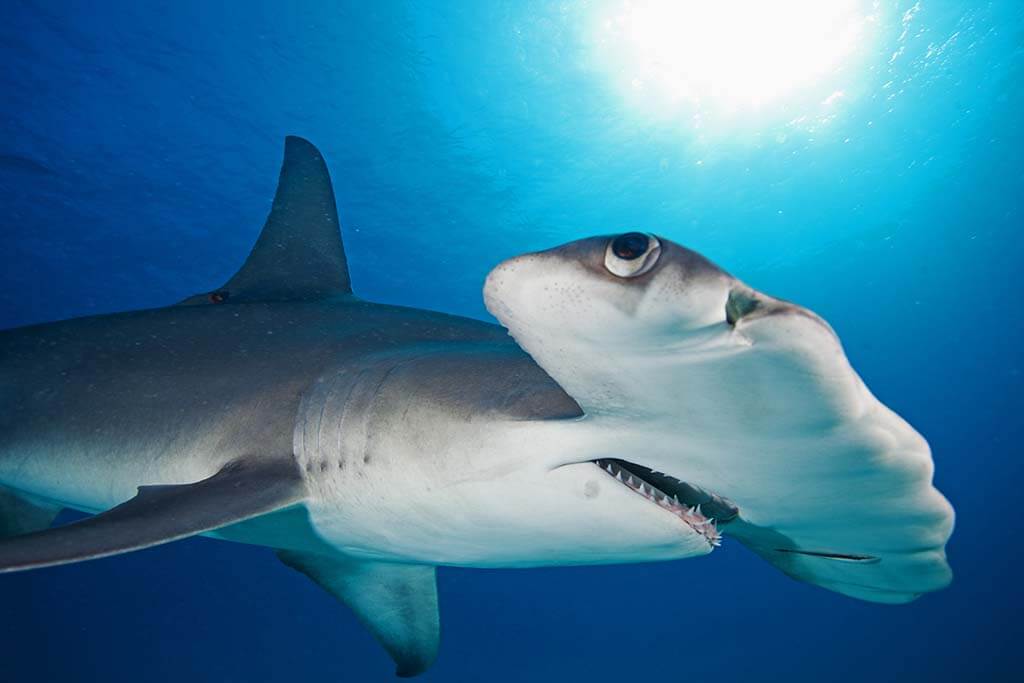

Great Hammerhead Shark Sphyrna Mokarran
The Great Hammerhead Shark was first described by Eduard Ruppell in 1837 but later changed its name to Sphyrna mokarran (S. mokarran). The name “Sphyrna” means “hammer” in Greek and refers to the shape of its head.
In 1950, Fraser-Brunner synonymized the species with Sphyrna ligo. There are ten related species, including the bonnethead (Sphyrna tiburo), scalloped hammerhead (Sphyrna mokarran), and ligo.
Thresher Shark Alopias Vulpinus 18.8 Feet
The thresher shark is not as well-known as many other types of sharks, but its massive tail can add as much as 18 feet to its length. This shark species can weigh up to 750 pounds and is found worldwide, including Hawaii. Whether you’re a shark enthusiast or looking for an unusual pet, the thresher may be just the thing to add to your collection.

Thresher Shark Alopias Vulpinus – Biggest Sharks In The World
This shark is ovoviviparous, meaning its eggs are laid inside its female. Pups are delivered at a length of about 1.5 meters (5 feet), after which they can begin to feed on their siblings. The thresher shark matures between three and eight years. Though it is a popular sport fish, the thresher shark is a nuisance to fishermen who are after mackerel.
Bluntnose Sixgill Shark Hexanchus Griseus 15 Feets
The bluntnose sixgill shark is a powerful predator. It prefers to spend the day in deep depths while foraging near the surface at night. The bluntnose sixgill shark feeds on various prey, including sizeable bony fish and invertebrates. It has been known to scavenge dead animals and even eat the bait from fishing longlines.
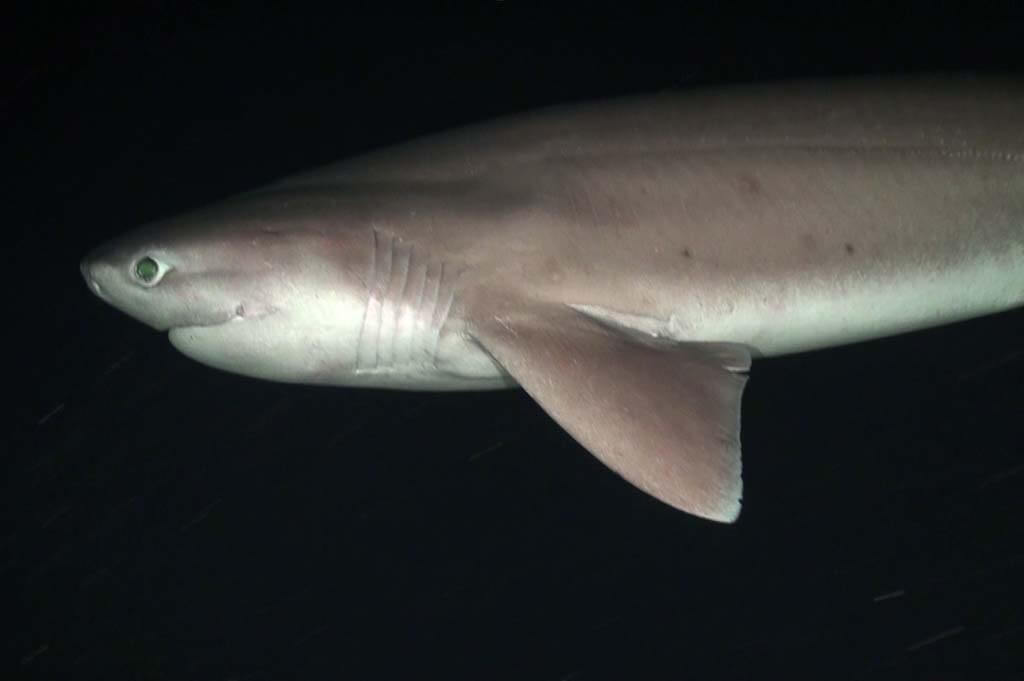

Bluntnose Sixgill Shark Hexanchus Griseus -Biggest Sharks In The World
The Hexanchus griseus has only one dorsal fin, which is situated behind the insertion point of its pelvic fins. The dorsal fin is long and rounded, while its pectoral fins are shorter and narrower.
The anal fin is smaller than the dorsal fin, and the pelvic fins have rounded tips and close-spaced margins. The bluntnose sixgill shark’s caudal peduncle is stout and short but does not stand out.
Pacific Sleeper Shark Somniosus Pacificus 14 Feets
The Pacific sleeper shark is a fascinating, slow-moving predator that inhabits the chilly, deep waters of the western and eastern Pacific Oceans. The species can grow to a length of 4.4 meters (14 ft) in the wild, although Fishbase accepts estimates of up to seven meters.
Because its body is thick, it can weigh up to 20 tons. This species is harmless to humans but produces toxins in its flesh.

Pacific Sleeper Shark Somniosus Pacificus Biggest Sharks In The World
This shark feeds on the carcasses of Grey Whales, which can be found every ten miles (16 kilometers) along its migration route. This abundance of protein and blubber provides a plentiful food source for the sleeper shark.
Because of its deep-adapted physiology, the shark has large olfactory bulbs and an excellent sense of smell. While this may sound unnerving, the Pacific Sleeper shark has been observed feeding on whale carcasses for hundreds of years.
Conclusion
Sharks have long been considered an ocean symbol and are among the largest fish species on Earth. They are referred to as pelagic in the ocean since they live in the water. These large fish are classified as either macrooceanic or tachypelagic. Their distributions are essentially circumglobal or disjunct. Some species live in both shallow and deep water.
Megalodon was once the world’s biggest fish, reaching a length of 18 meters. Its teeth resemble modern great white sharks, so it’s possible that it resembled them, too. Although only the teeth of megalodon have survived, they are three times longer than the teeth of a great white shark. Therefore, they were larger than our modern great white shark.
Maybe you also like:













